
Therefore the alveoli at the bottom of the lung increase their volume more with each inspiration and decrease their volume more with each expiration during eupnea (from FRC).ĭead space ventilation is a necessary part of the process of ventilating the alveoli and is not totally wasted. Therefore the alveoli at the top of the lung are at a higher, less compliant point on the pressure-volume curve than those at the bottom. Therefore the trans-pulmonary pressure gradient is greater at the top of the lung than at the bottom. Intrapleural (intrathoracic) pressure is less negative at the bottom of the lung than at the top because of the weight of the lung and the configuration of the chest wall. More ventilation of lower (with respect to gravity) regions of the lung than upper regions of the lung. Therefore, the tidal volume has a dead space component and an alveolar component. Physiologic dead space is defined as the volume of gas that is inspired but takes no part in gas exchange in the airways and alveoli.
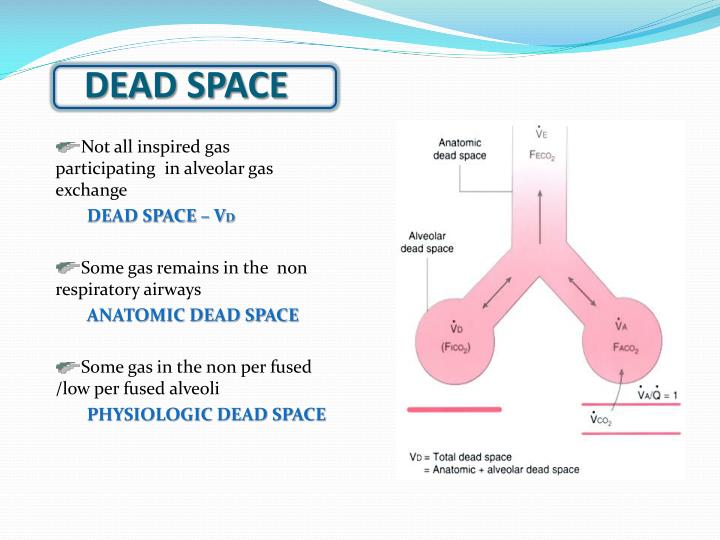
is referred to as physiologic dead space.

Ventilation of nonperfused alveoli and the airways, because neither accomplishes exchange of the respiratory gases. Ventilating these alveoli is ineffective in producing changes in the blood gases. The other part of dead space ventilation is made up of alveoli with diminished capillary perfusion. Because there is little or no diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the membranes of most of the airways, they compose part of dead space.
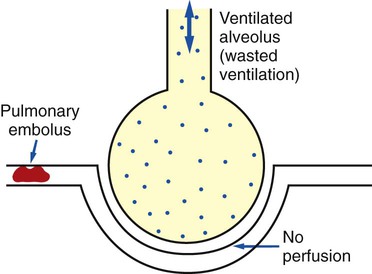
The tidal volume is used to ventilate not only the alveoli, but also the airways leading to the alveoli.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
